Testimonial: Iranian Global-PPS of Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance
 In 2011, Iran started conducting it’s first Point Prevalence Survey (PPS) in Kurdistan during a pilot project. The following year, this was extended to Shiraz as part of the ARPEC study. This study focused on developing hospital-quality indicators of antibiotic prescribing for children with the help of a PPS.
In 2011, Iran started conducting it’s first Point Prevalence Survey (PPS) in Kurdistan during a pilot project. The following year, this was extended to Shiraz as part of the ARPEC study. This study focused on developing hospital-quality indicators of antibiotic prescribing for children with the help of a PPS.
Start of the Global-PPS in Iran
The Global-PPS in Iran primarily started in 2015 in the Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences, concurrently with the first global attempt for data collection about antibiotic consumption conducted by the University of Antwerp, Belgium. From 2017, the Global-PPS was repeated every year with additional data collected in 4 new hospitals in Sanandaj.
Results
The Global-PPS showed an unfavorable situation of prescribing behaviors in Iran compared to EU countries. The main problems include high broad-spectrum antibiotic prescribing with poor results on a set of quality indicators of antibiotic use, such as poor adherence to empirical guidelines and lack of diagnostic capacity.
These results have been presented at several international conferences in Iran organized by Prof. Alborzi Clinical Microbiology Research Center and during the last European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. By doing so, we hope to promote antibiotic stewardship programmes in Iran.
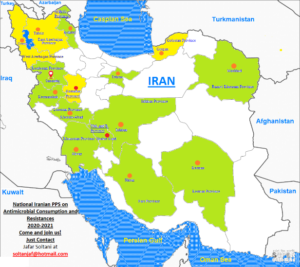
The Iranian national network on antibiotic consumption and resistance
The results also showed that there is an urgent need to develop and disseminate a National Antibiotic Stewardship Action plan. For that reason, a national workshop, moderated by Dr. Jafar Soltani, was conducted during the 13th International Alborzi Congress of Clinical Microbiology in Shiraz, October 2019. Pediatric infectious subspecialists, adult infectious diseases specialists and microbiologists from all over Iran participated in the workshop.
During the workshop, we set up a national network to study antibiotic consumption and resistance in Iran using the standardised methodology of the Global-PPS. Participants from different parts of the country were designated as provincial focal points. In addition, it was decided that all data would be collected in a subset under the name “National Iranian Point prevalence study”.
The Global-PPS is now being implemented for the first time, depending on the city.


MUK Team from left to right:
Standing – Dr. Jafar Soltani, Dr. Borhan Moradvaeisi (Besat Hospital Head), Dr. Ghafari (Pediatric Resident).
Sittting – Dr. Borna (Pediatric Resident), Dr. Mehrnaz Aligholipour, Dr. Kani Javedan, Ms. Soraya Mollaei.